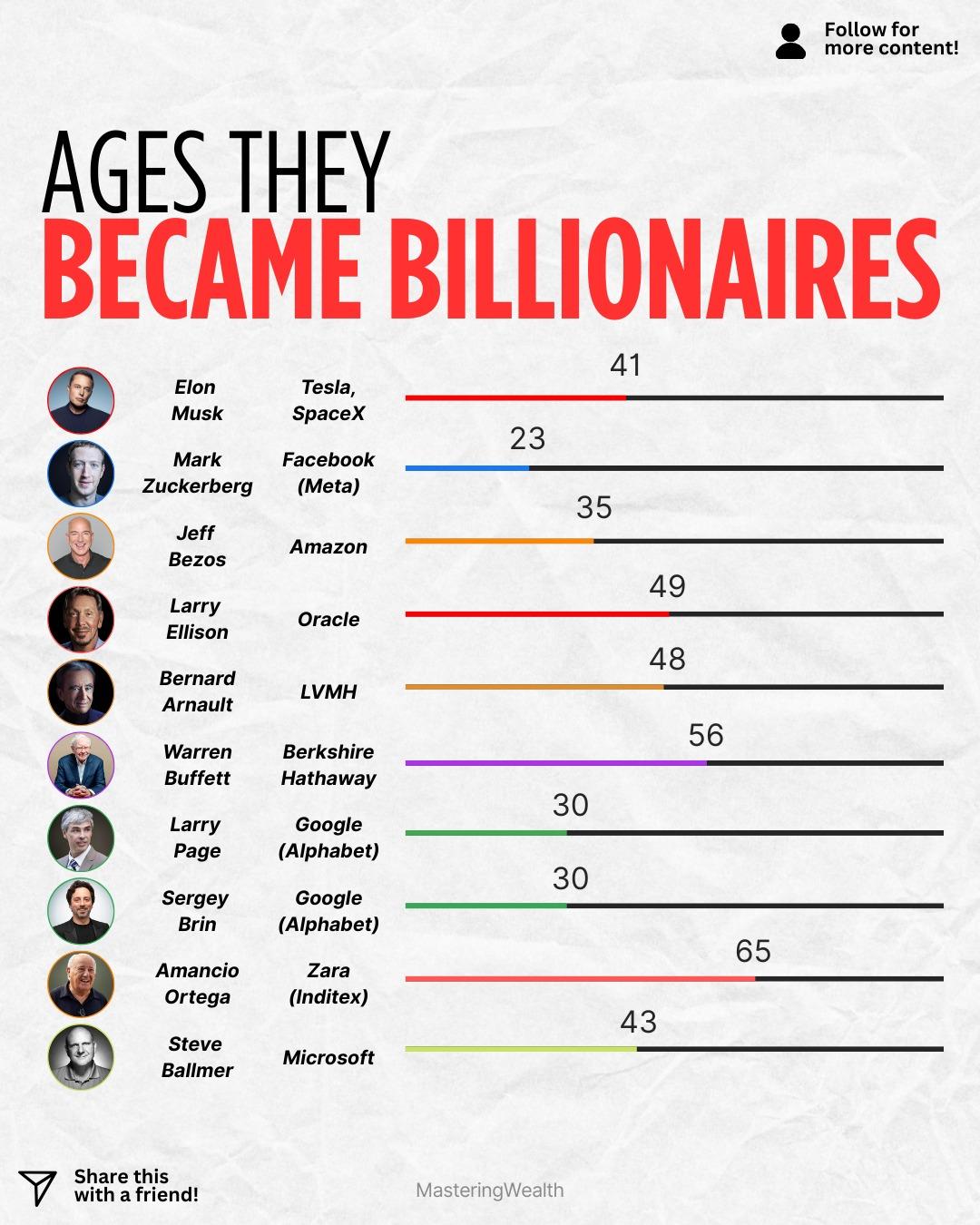
Success does not have a deadline. The graphic in this post shows the ages at which some of the world’s most famous entrepreneurs became billionaires. What it proves is that wealth can be created early, late, and everywhere in between depending on timing, vision, and perseverance.
Mark Zuckerberg became a billionaire at age twenty three which makes him one of the youngest on the list. Sergey Brin and Larry Page reached billionaire status at age thirty through Google. Jeff Bezos reached his billionaire milestone at age thirty five after years of building Amazon when online shopping was still a new idea.
Others reached the milestone later in life. Elon Musk became a billionaire at forty one while scaling Tesla and SpaceX after many failures and setbacks. Bernard Arnault reached billionaire status at forty eight through luxury brands and long term business thinking.
Some reached the milestone even later. Warren Buffett became a billionaire at age fifty six after decades of consistent investing and value based decisions. Amancio Ortega, the founder of Zara, became a billionaire at age sixty five which shows that massive wealth can still be built late in life.
This list proves that there is no perfect age for success. What matters is the willingness to start, learn, take risks, and keep going. The timeline looks different for everyone but persistence always pays off somewhere along the journey.
Comment “Stocks” if you want a link to see my dividend portfolio and learn how long term investing builds wealth step by step.
If you could choose any path toward financial freedom, would you prefer the fast route with higher risk or the slow and steady route like Warren Buffett?
For more visuals that break down success stories, wealth building, and investing lessons, follow @MasteringWealth for daily financial content.
This content is for educational purposes only and is not financial advice. Always research carefully or consult with a licensed professional before making investment decisions.
Mark Zuckerberg became a billionaire at age twenty three which makes him one of the youngest on the list. Sergey Brin and Larry Page reached billionaire status at age thirty through Google. Jeff Bezos reached his billionaire milestone at age thirty five after years of building Amazon when online shopping was still a new idea.
Others reached the milestone later in life. Elon Musk became a billionaire at forty one while scaling Tesla and SpaceX after many failures and setbacks. Bernard Arnault reached billionaire status at forty eight through luxury brands and long term business thinking.
Some reached the milestone even later. Warren Buffett became a billionaire at age fifty six after decades of consistent investing and value based decisions. Amancio Ortega, the founder of Zara, became a billionaire at age sixty five which shows that massive wealth can still be built late in life.
This list proves that there is no perfect age for success. What matters is the willingness to start, learn, take risks, and keep going. The timeline looks different for everyone but persistence always pays off somewhere along the journey.
Comment “Stocks” if you want a link to see my dividend portfolio and learn how long term investing builds wealth step by step.
If you could choose any path toward financial freedom, would you prefer the fast route with higher risk or the slow and steady route like Warren Buffett?
For more visuals that break down success stories, wealth building, and investing lessons, follow @MasteringWealth for daily financial content.
This content is for educational purposes only and is not financial advice. Always research carefully or consult with a licensed professional before making investment decisions.
Success does not have a deadline. The graphic in this post shows the ages at which some of the world’s most famous entrepreneurs became billionaires. What it proves is that wealth can be created early, late, and everywhere in between depending on timing, vision, and perseverance.
Mark Zuckerberg became a billionaire at age twenty three which makes him one of the youngest on the list. Sergey Brin and Larry Page reached billionaire status at age thirty through Google. Jeff Bezos reached his billionaire milestone at age thirty five after years of building Amazon when online shopping was still a new idea.
Others reached the milestone later in life. Elon Musk became a billionaire at forty one while scaling Tesla and SpaceX after many failures and setbacks. Bernard Arnault reached billionaire status at forty eight through luxury brands and long term business thinking.
Some reached the milestone even later. Warren Buffett became a billionaire at age fifty six after decades of consistent investing and value based decisions. Amancio Ortega, the founder of Zara, became a billionaire at age sixty five which shows that massive wealth can still be built late in life.
This list proves that there is no perfect age for success. What matters is the willingness to start, learn, take risks, and keep going. The timeline looks different for everyone but persistence always pays off somewhere along the journey.
💬 Comment “Stocks” if you want a link to see my dividend portfolio and learn how long term investing builds wealth step by step.
If you could choose any path toward financial freedom, would you prefer the fast route with higher risk or the slow and steady route like Warren Buffett?
For more visuals that break down success stories, wealth building, and investing lessons, follow @MasteringWealth for daily financial content.
⚠️ This content is for educational purposes only and is not financial advice. Always research carefully or consult with a licensed professional before making investment decisions.
·297 Просмотры
·0 предпросмотр